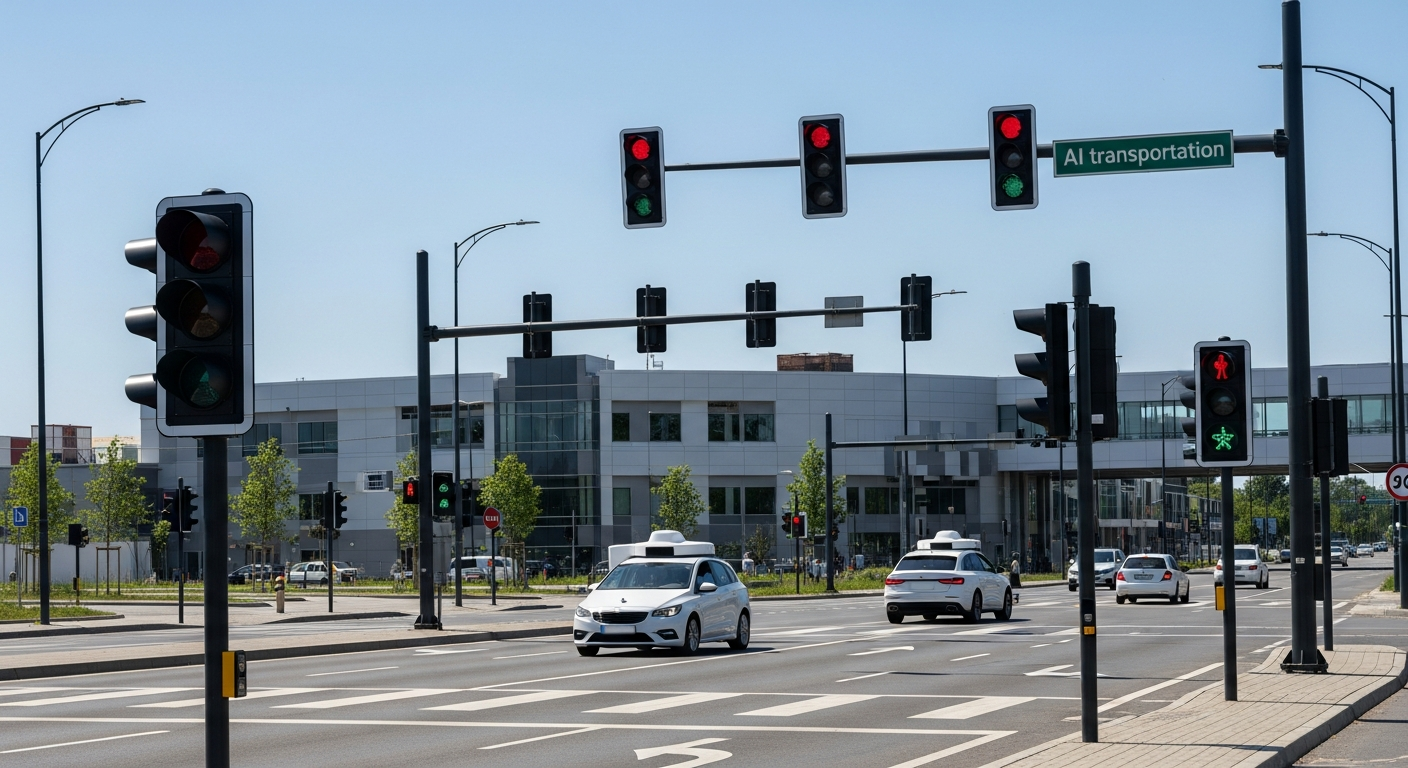

AI in transportation, including smart traffic lights and self-driving cars.
- November 20, 2025
- ~ 1 min read
- 71 views
- Smart Cities , Everyday AI
Introduction: Navigating the Future with AI in Transportation
Picture this: a morning commute without soul-crushing traffic, city streets where accidents are a rare anomaly, and public transit that anticipates your needs. For too long, our global transportation systems have grappled with a myriad of challenges – relentless congestion, environmental pollution, the tragic toll of accidents, and inefficient resource allocation. These roadblocks not only hinder productivity but also diminish our quality of life, making the quest for smarter, safer, and more sustainable mobility solutions increasingly urgent.
The Current Roadblocks and AI's Promise
In this era of unprecedented technological advancement, one force stands poised to fundamentally rewrite the narrative of our daily journeys: Artificial Intelligence. Far more than just a buzzword, AI in transportation is the revolutionary backbone that promises to transform how we move people and goods across the globe. It’s about leveraging vast datasets, advanced algorithms, and machine learning capabilities to predict patterns, optimize routes, enhance safety protocols, and even operate vehicles autonomously. The potential for AI to create truly smart cities, where every aspect of mobility is integrated and responsive, is not just a dream but a rapidly approaching reality.
The integration of AI into our infrastructure represents a critical paradigm shift, moving us from reactive problem-solving to proactive, predictive management. This is why understanding the profound AI impact on our transit systems is no longer optional but essential for anyone invested in the future of mobility.
What You'll Discover in This Journey
This article will serve as your comprehensive guide to the cutting-edge landscape of intelligent transport systems. We will delve into specific, transformative innovations that are already redefining our experience, prominently featuring the dynamic capabilities of smart traffic lights that adapt to real-time conditions and the sophisticated algorithms powering self-driving cars that promise unparalleled safety and convenience. You'll gain insights into the technology, its benefits, the challenges ahead, and what it means for our collective future. Prepare to navigate the exciting intersection of AI and transportation, and discover how this powerful technology is paving the way for a more efficient, equitable, and safer world on the move.
Main Content: Decoding AI's Core Function in Modern Transport
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into transportation isn't just about adding new gadgets; it fundamentally transforms how vehicles move and how infrastructure manages their flow. At its core, AI brings a paradigm shift from static, predetermined operations to dynamic, data-driven decision-making. This section delves into the intricate mechanisms of how AI operates within two pivotal areas: smart traffic lights and self-driving cars, underpinned by critical technologies.
The Fundamentals of AI in Traffic Management
Traditional traffic systems rely on fixed timers or rudimentary sensors that trigger pre-programmed responses. In contrast, AI traffic management leverages vast amounts of real-time data to make intelligent, adaptive decisions. This data includes everything from vehicle count and speed to pedestrian movement, weather conditions, and even historical traffic patterns. AI algorithms process this information instantaneously, learning from past scenarios and predicting future trends to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and enhance safety across urban networks. It's about moving from reactive measures to proactive, predictive control, making our roads significantly more efficient and responsive to actual conditions.
Smart Traffic Lights: Precision through Real-time Data
Imagine traffic lights that don't just follow a schedule but understand the flow of vehicles and pedestrians. This is the promise of smart traffic lights AI. Their mechanism involves a sophisticated array of sensors, including inductive loops embedded in the road, cameras that perform computer vision analysis, and even radar or LiDAR units. These sensors continuously collect real-time data on everything happening at an intersection: the number of cars waiting in each lane, their speed, the presence of emergency vehicles, and pedestrian crossings.
This deluge of data feeds into advanced machine learning algorithms. Unlike conventional systems, these algorithms don't just react; they predict. They analyze patterns, identify bottlenecks before they fully form, and dynamically adjust signal timings to optimize throughput. For instance, if one direction has a heavy backlog while another is clear, the AI can extend the green light for the congested lane, significantly reducing waiting times and minimizing idling. This dynamic adjustment leads to substantial reductions in urban congestion and associated carbon emissions, showcasing the tangible benefits of machine learning in transport infrastructure.
Self-Driving Cars: The AI Pipeline from Perception to Control
The development of self-driving car technology represents one of AI's most ambitious applications. Autonomous vehicles operate through a complex, multi-stage AI pipeline that allows them to perceive their environment, predict future events, plan a course of action, and execute it safely.
- Perception: This is the car's ability to "see" and understand its surroundings. It relies on a suite of sensors—cameras, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, and ultrasonic sensors—that gather raw data. AI-powered computer vision and other algorithms then process this data to identify objects like other vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists, lane markings, traffic signs, and road conditions.
- Prediction: Once objects are identified, the AI must predict their future behavior. For example, will that pedestrian step onto the road? Is the car in the next lane about to merge? Sophisticated machine learning models analyze motion patterns and historical data to forecast the probable trajectories and intentions of dynamic agents in the environment, which is crucial for safe navigation.
- Planning: Based on the perceived environment and predicted actions of other agents, the AI system formulates a safe and efficient path. This involves complex autonomous driving algorithms that consider navigation goals, traffic laws, comfort for passengers, and potential risks. The planning module decides on actions such as acceleration, braking, lane changes, turns, and obstacle avoidance maneuvers.
- Control: Finally, the control module translates the high-level plans into specific vehicle commands. This means precisely actuating the steering, throttle, and brakes to execute the planned trajectory smoothly and accurately. The control system continuously monitors the vehicle's actual movement against the planned movement, making micro-adjustments in real time.
Underlying Technologies Fueling the AI Revolution
Several foundational technologies make the intelligent operations of smart traffic lights and self-driving cars possible:
- Computer Vision: This field of AI enables machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world, playing a crucial role in cameras used for both traffic monitoring and autonomous vehicle perception. It allows for object detection, classification, and tracking.
- Machine Learning (ML) & Deep Learning: These are the brains behind prediction and decision-making. From recognizing patterns in traffic flow to enabling a self-driving car to learn from vast datasets, ML algorithms (especially deep neural networks) are indispensable for processing complex data and making adaptive choices.
- Sensor Fusion: A critical technique where data from multiple types of sensors (e.g., cameras, radar, LiDAR) is combined and processed to create a more complete, accurate, and robust understanding of the environment than any single sensor could provide alone. Sensor fusion mitigates the limitations of individual sensors, enhancing reliability and safety.
- Edge AI: To ensure instantaneous decision-making, particularly in safety-critical applications like self-driving cars and real-time traffic control, AI processing often happens directly on the device or at the "edge" of the network rather than in a distant cloud. This reduces latency, improves responsiveness, and enhances privacy and security.
The synergistic integration of these advanced AI components and underlying technologies is precisely what propels modern transportation into an era of unprecedented efficiency, safety, and autonomy.
Supporting Content: Real-World Applications & Case Studies
The theoretical promise of AI in transportation is compelling, but its true impact is best understood through tangible, real-world applications. From smart city initiatives to autonomous fleets, AI is already reshaping how we move, deliver goods, and manage complex traffic flows. These deployments offer invaluable insights into the transformative power of artificial intelligence.
Adaptive Traffic Signal Systems: Smarter City Flows
One of the most immediate and impactful applications of AI in urban environments has been the development and deployment of smart traffic case studies. These systems leverage AI algorithms to optimize traffic flow in real-time, moving beyond static timing patterns to dynamic adjustments based on current conditions.
- Pittsburgh's Surtrac System: One of the pioneering efforts in adaptive traffic control, the Surtrac (Scalable Urban & Rural Traffic Control) system developed by Carnegie Mellon University spin-off, Rapid Flow Technologies, has revolutionized traffic management in Pittsburgh. Deployed at intersections across the city, Surtrac uses AI to process data from sensors, radar, and cameras, predicting traffic demand and adjusting signal timings to minimize wait times and congestion. The results have been remarkable: evaluations have shown a reduction in travel time by up to 25%, idle time by 40%, and emissions by 20%, demonstrating the profound effect AI can have on urban mobility.
- Sydney's SCATS System: The Sydney Coordinated Adaptive Traffic System (SCATS) is another globally recognized example, operational in hundreds of cities worldwide. While not as purely AI-driven as Surtrac in its earliest iterations, SCATS has evolved to incorporate advanced algorithms that adapt signal timings across a network of intersections. It continuously monitors traffic volume and occupancy, making micro-adjustments to optimize flow, especially during peak hours or unexpected disruptions. Its long-standing success underscores the value of intelligent traffic management.
These systems are prime examples of how AI can bring significant efficiency gains and environmental benefits to our bustling cities, making daily commutes smoother and more sustainable.
Autonomous Vehicles on Our Streets: From Robotaxis to Deliveries
The vision of self-driving cars is rapidly transitioning from science fiction to everyday reality, with numerous autonomous vehicle deployments now operating in select cities. These vehicles, powered by sophisticated AI, machine learning, and sensor fusion technologies, are paving the way for a new era of mobility.
- Waymo: A subsidiary of Alphabet (Google's parent company), Waymo is a frontrunner in autonomous technology. After years of extensive testing, Waymo launched the world's first fully autonomous public robotaxi service in Phoenix, Arizona, and has since expanded operations to San Francisco and Los Angeles. Its vehicles operate at SAE Level 4 autonomy, meaning they can handle all driving tasks under specific conditions without human intervention. Waymo's consistent performance highlights the maturity of AI in navigating complex urban environments.
- Cruise: Backed by General Motors, Cruise has been another key player in the robotaxi space, particularly active in San Francisco. While facing challenges and temporary operational pauses, Cruise's deployments have showcased the immense potential of AI to provide ride-hailing services. Their vehicles also aim for Level 4 autonomy, offering driverless rides to the public, underscoring the shift towards autonomous public transport solutions.
- Nuro: Focusing on autonomous last-mile delivery, Nuro utilizes custom-built, smaller autonomous vehicles designed specifically for transporting goods. With partnerships with major retailers and restaurants, Nuro's driverless vehicles are becoming a common sight in areas like Houston and Mountain View, demonstrating AI's role in optimizing logistics and contactless delivery services. This specialization highlights the diverse applications of self-driving technology beyond passenger transport.
These deployments, despite ongoing regulatory and technical hurdles, clearly demonstrate the tangible progress in autonomous driving, fueled by advanced AI algorithms.
Optimizing Operations: AI in Logistics and Beyond
Beyond individual vehicles and traffic signals, AI is revolutionizing the broader ecosystem of transportation and logistics, driving efficiencies and enabling new services.
- AI in Logistics and Fleet Management: For commercial fleets, AI logistics solutions are transforming route planning, dispatch, and operational efficiency. Algorithms analyze vast datasets including real-time traffic, weather, delivery windows, driver availability, and vehicle capacity to generate optimal routes. This not only significantly reduces fuel consumption and travel times but also minimizes environmental impact. Companies utilize AI to manage complex supply chains, predict demand, and even optimize warehouse operations, showcasing AI's holistic impact on freight movement.
- Predictive Maintenance Transport: AI is also playing a critical role in maintaining the reliability and safety of vehicles through predictive maintenance transport. By continuously monitoring data from vehicle sensors (engine performance, tire pressure, brake wear, etc.), AI models can detect subtle anomalies and predict potential equipment failures *before* they occur. This allows fleet operators to schedule maintenance proactively, reducing costly unplanned downtime, extending vehicle lifespan, and enhancing safety for trucks, buses, and trains alike.
- Emerging Applications in Public Transport: AI is increasingly being used to optimize public transport. From dynamic scheduling of buses and trains based on real-time demand and passenger flow, to forecasting ridership patterns to better allocate resources, AI ensures public transit systems are more responsive, efficient, and user-friendly. This includes demand-responsive transit systems that use AI to optimize routes and schedules for on-demand services, bridging gaps in traditional fixed-route services.
These applications underscore AI's versatile capabilities, extending its influence across the entire transportation spectrum to create smarter, more efficient, and safer mobility solutions.
Advanced Content: Technical Deep Dive & Emerging Challenges
As AI continues to redefine the transportation landscape, a closer examination of its underlying technical complexities and the significant hurdles to widespread adoption reveals the true scope of this revolution. This section delves into the sophisticated algorithms driving smart mobility, the intricate architectures of autonomous systems, and the crucial non-technical considerations that will shape the future of urban and interurban travel.
Core AI Architectures and Algorithms
At the heart of intelligent transportation lies a suite of advanced AI algorithms. For dynamic traffic management, systems often employ reinforcement learning traffic optimization. Here, an AI agent, representing a traffic light or a network controller, learns optimal signal timings by interacting with the environment. States are defined by real-time traffic density, queue lengths, and historical patterns, while actions involve adjusting signal phases and durations. The reward function is typically engineered to minimize congestion, travel time, and emissions across the network. Multi-agent systems extend this, allowing individual intersections or even vehicle platoons to act as cooperative agents, optimizing both local and global traffic flow in a decentralized manner.
Autonomous vehicles, conversely, rely on a robust technical stack for perception, localization, and motion planning. Autonomous vehicle perception involves fusing data from multiple sensors—LiDAR, radar, cameras, ultrasonic—to create a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle's surroundings. Deep learning architectures like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and increasingly Transformers process this raw sensor data for object detection, segmentation, and semantic understanding. For precise positioning within a dynamic environment, Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) algorithms are paramount. These systems use techniques like point cloud registration (ICP), visual odometry, and filtering (Extended Kalman Filters, particle filters) to build and update maps while simultaneously tracking the vehicle's exact position. Motion planning then leverages this rich environmental model to calculate safe, efficient, and comfortable trajectories, often incorporating predictive models for pedestrian and other vehicle behavior.
Navigating the Future: Challenges, Infrastructure, and Governance
The deployment of AI in transportation introduces multifaceted challenges spanning data privacy, cybersecurity, and ethics. Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) generate colossal volumes of data on vehicle movements, passenger habits, and infrastructure usage, necessitating stringent data privacy frameworks like GDPR and innovative privacy-preserving techniques such as federated learning or differential privacy. On the cybersecurity front, the interconnected nature of ITS and autonomous vehicles creates new attack vectors. Robust cybersecurity ITS strategies are critical to prevent sensor spoofing, denial-of-service attacks on V2X communication, or malicious control system takeovers. This requires state-of-the-art encryption, intrusion detection systems, and secure over-the-air (OTA) update mechanisms. Furthermore, AI ethics transport dilemmas, particularly concerning autonomous vehicle accident scenarios, demand transparent and explainable decision-making processes. Establishing clear accountability and ensuring fairness in algorithmic outcomes are paramount for public trust and legal acceptance.
To enable scalable deployment, a powerful infrastructure backbone is essential. Fifth-generation (5G) cellular networks provide the low-latency, high-bandwidth connectivity vital for real-time data exchange in V2X communication (Vehicle-to-Vehicle, Vehicle-to-Infrastructure, Vehicle-to-Pedestrian, Vehicle-to-Network). This allows vehicles to share sensor data, intent, and warnings, enhancing situational awareness far beyond line-of-sight. Complementing this, digital twins transport systems offer real-time virtual replicas of entire urban traffic networks or individual vehicles. These digital twins serve as powerful simulation environments for predictive maintenance, traffic optimization, and the development and testing of new AI models without physical deployment.
Finally, the complex and evolving regulatory AI transport landscape presents a significant hurdle. A lack of uniform global standards for autonomous vehicle testing, certification, and operation can hinder cross-border deployment. International bodies like the UNECE, ISO, and IEEE are working towards standardizing operational design domains (ODDs), safety requirements, and communication protocols. Harmonizing these regulations is crucial for fostering innovation, ensuring safety, and building public confidence in AI-driven transportation systems.
Practical Content: Implementation Strategies & Best Practices
Implementing AI-driven solutions in transportation is a complex yet highly rewarding endeavor. For stakeholders, from city planners to automotive manufacturers, a structured approach is paramount to navigate the technical, financial, and social landscapes. This section outlines actionable strategies, best practices, and key considerations for successfully integrating AI into urban mobility and vehicle ecosystems.
Phased Implementation of Smart Traffic Systems & Autonomous Vehicle Ecosystems
Adopting smart traffic solutions requires a strategic, incremental rollout to ensure smooth integration and maximum benefit. Cities should begin with a thorough understanding of their specific needs and existing infrastructure.
- Feasibility Studies & Needs Assessment: Initiate with comprehensive studies to identify current traffic bottlenecks, public transport challenges, and data gaps. Assess existing infrastructure capabilities and potential integration points for AI systems. This phase helps define clear objectives and measurable outcomes for any new deployment.
- Pilot Programs & Proof of Concept: Before full-scale deployment, launch targeted pilot programs. For instance, implement adaptive traffic signals in a specific high-congestion corridor or test AI-powered public transport routing on a limited route. These pilots provide valuable real-world data, allow for iterative improvements, and build confidence among stakeholders and the public.
- Data Governance & Integration: A robust framework for collecting, processing, and storing traffic data is crucial. Ensure new AI systems can seamlessly integrate with existing transportation management platforms. Establish clear policies for data privacy, security, and access, prioritizing transparent use of information gathered for enhanced urban mobility.
- Phased Rollout & Scalability: Based on successful pilot outcomes, gradually expand the smart traffic system across the city. This phased approach allows for continuous learning, adaptation to local conditions, and optimized resource allocation. Focusing on smart city implementation from a modular perspective ensures scalability and future-proofing.
Simultaneously, developing an ecosystem for autonomous vehicles (AVs) demands significant infrastructure and policy evolution. Critical investments in V2I infrastructure (Vehicle-to-Infrastructure communication), such as smart sensors, high-bandwidth connectivity, and dedicated charging stations for electric AVs, are essential. Alongside physical upgrades, progressive autonomous vehicle policy frameworks are needed to address legal liability, operational standards, testing regulations, and data sharing protocols. Proactive policy development encourages innovation while safeguarding public safety.
Data-Driven Decisions and Societal Integration
The success of AI in transportation hinges on intelligent data management and careful consideration of human factors. Effective transport data analytics forms the backbone of any smart mobility initiative.
- Best Practices for Data Management:
- Real-time Collection & Processing: Implement sensors, cameras, and IoT devices to gather continuous, real-time data on traffic flow, pedestrian movement, public transport usage, and environmental conditions.
- Advanced Analytics & Predictive Modeling: Leverage AI and machine learning to analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, predict congestion, optimize routes, and forecast demand. This allows for proactive decision-making rather than reactive responses.
- Data Security & Privacy: Adhere to strict cybersecurity protocols and privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR) to protect sensitive personal and operational data. Transparency about data usage builds public trust.
- Interoperability: Ensure different data sources and systems can communicate and share information effectively to create a holistic view of the transportation network.
Addressing public acceptance AI and workforce transition are equally vital for smooth integration. Proactive communication campaigns, educational programs, and community engagement forums can demystify AI technologies, highlight their benefits, and address public concerns regarding safety, privacy, and job displacement. For the existing workforce, strategies for workforce transition transport should include comprehensive reskilling and upskilling programs. These programs can prepare employees for new roles in AI system maintenance, data analysis, ethical oversight, and smart infrastructure management, ensuring a just transition rather than significant job losses.
Key Considerations: Funding, Partnerships & Scalability
Sustainable implementation of AI in transportation requires innovative funding models and collaborative partnerships.
- Funding Models: Cities and organizations should explore diverse funding avenues beyond traditional budgets. This includes government grants for intelligent transportation systems (ITS funding), green bonds for sustainable initiatives, and even user-based fees where appropriate. Creative financial instruments can kickstart crucial projects.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Collaborations between public entities and private companies are often the most effective way to combine expertise, share risks, and accelerate deployment. Private sector partners can bring cutting-edge technology, innovation, and investment, while public partners provide regulatory oversight, infrastructure, and community engagement.
- Scalability and Long-Term Vision: Design AI solutions with scalability in mind, allowing for future expansion and integration of new technologies. Develop a long-term vision that anticipates evolving urban needs and technological advancements, ensuring that initial investments continue to yield benefits for decades to come. A forward-thinking strategy is key to building resilient and efficient transportation systems.
Comparison & Analysis: Benefits, Challenges, and the Road Ahead
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into transportation marks a pivotal shift, promising a future of unparalleled efficiency and safety. However, this transformative journey is not without its complexities. A balanced analysis reveals both profound advantages and significant hurdles that demand careful consideration as we pave the way for intelligent mobility systems.
Major Benefits: A Leap Towards Smarter, Safer Mobility
The advent of AI-powered transportation systems brings forth an array of compelling advantages:
- Enhanced Safety: Perhaps the most profound of all AI transport benefits is the potential for drastically reduced accident rates. Self-driving cars, equipped with sophisticated sensors and predictive algorithms, can eliminate human error—fatigue, distraction, and impairment—which accounts for over 90% of road accidents. Smart traffic lights, on the other hand, dynamically adjust to real-time traffic conditions, preventing collisions at intersections and improving overall flow. This directly translates to superior autonomous vehicle safety and safer urban environments.
- Reduced Congestion & Emissions: AI algorithms excel at optimizing traffic flow. Smart traffic lights, for instance, coordinate signals across an entire city to minimize wait times and keep traffic moving smoothly. Similarly, AI-powered navigation and fleet management systems can suggest optimal routes, reducing vehicle idle time and overall travel distances. The resulting decrease in stop-and-go traffic leads to significant congestion reduction AI benefits, lowering fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, thereby contributing to cleaner air.
- Improved Accessibility: AI in transport holds the promise of greater mobility for everyone. Autonomous vehicles can provide independent transportation for the elderly, individuals with disabilities, and those who cannot drive, expanding access to essential services and opportunities. AI-optimized public transport systems can also better serve underserved areas, ensuring more equitable access to mobility.
Key Challenges: Navigating the Roadblocks
Despite the revolutionary potential, the deployment of AI in transportation faces substantial obstacles:
- High Implementation Costs: Developing, testing, and deploying robust AI transportation infrastructure demands immense financial investment. This includes not only the vehicles themselves but also the necessary digital infrastructure, high-definition mapping, sensor networks, and advanced communication systems, making widespread adoption a costly endeavor.
- Data Security Risks: AI systems are inherently data-driven. The vast amounts of data collected and processed—from vehicle telemetry to personal travel patterns—present significant cybersecurity challenges. A successful cyber-attack on autonomous vehicles or smart traffic grids could lead to widespread disruption, safety compromises, or even national security threats. Robust, multi-layered security protocols are paramount.
- Job Displacement Concerns: The rise of autonomous vehicles, particularly in freight and ride-sharing, raises valid concerns about job displacement AI will bring to sectors traditionally reliant on human drivers. Policymakers and industry leaders must proactively address these socio-economic impacts through retraining programs and new job creation initiatives.
Societal and Ethical Dilemmas: The Human Equation
Beyond the technical and economic hurdles, AI in transport introduces complex societal and ethical considerations:
- The 'Trolley Problem' for AVs: Autonomous vehicles will inevitably encounter scenarios where they must make split-second decisions in unavoidable accident situations. Programming an AV to prioritize certain outcomes—e.g., protecting its occupants versus minimizing harm to pedestrians, or choosing between two different harms—brings forth the classic 'Trolley Problem' into real-world engineering. This highlights the critical need for an ethical framework guiding AI decisions.
- Equity in Access to Smart Transport: As AI transforms urban mobility, ensuring equitable access to these advanced services is crucial. There's a risk that the benefits of smart traffic systems and autonomous fleets could disproportionately favor affluent areas or individuals, exacerbating existing societal inequalities. Policymakers must proactively design systems that promote inclusivity and universal access.
Comparative Analysis: Public vs. Private AI Applications
AI's application varies significantly between public and private transportation:
For public transport AI, the focus is on optimizing large-scale systems. This includes AI-powered route optimization and dynamic scheduling for buses and trains, predictive maintenance to prevent service disruptions, and intelligent demand-responsive transit solutions that adapt to passenger needs in real-time. The goal is to move a high volume of people efficiently, reduce operational costs, and enhance the overall public transit experience for an entire city or region.
Conversely, in private transportation, AI primarily enhances individual mobility. Personal autonomous vehicles offer unparalleled convenience, door-to-door service, and personalized travel experiences. AI also plays a role in optimizing individual vehicle performance, energy consumption, and parking. While offering individual freedom, the challenge lies in ensuring that a proliferation of personal AVs doesn't exacerbate urban congestion or parking issues, unless integrated seamlessly with smart city infrastructure.
The Human Element: Balancing Innovation with Oversight
As AI assumes more control, the human element remains indispensable. While AI excels at processing vast data and making rapid decisions, human oversight and intervention are vital, particularly in unforeseen "edge cases" or emergencies that AI might not be programmed to handle. Future systems will likely feature a blend of advanced AI with remote human monitoring capabilities, allowing for intervention when necessary. Maintaining a human in the loop not only provides a crucial safety net but also fosters public trust and acceptance, which are paramount for the successful, widespread adoption of AI in transportation. The design of these systems must be human-centric, ensuring transparency, explainability, and the ability for human operators to understand and, if required, override AI decisions.
Conclusion: The Path to a Hyper-Connected Future of Transportation
Reimagining Mobility: AI's Transformative Impact
Throughout this article, we've journeyed into the heart of AI's profound impact on transportation, witnessing its power to redefine everything from urban commutes to long-haul logistics. From the dynamic optimization offered by smart traffic lights that fluidly manage urban flow, to the groundbreaking autonomy of self-driving cars promising unparalleled safety and convenience, it's clear that AI is not merely an enhancement; it is a fundamental reinvention of how we move. We've seen how AI innovation is paving the way for significantly reduced congestion, enhanced road safety, and a more efficient use of our existing infrastructure, laying the groundwork for a truly modern transportation paradigm.
Towards an Intelligent, Sustainable Tomorrow
The vision is clear: a fully integrated, intelligent, and sustainable mobility ecosystem where vehicles communicate seamlessly with infrastructure, and real-time data drives optimal decisions across the entire network. This is the promise of the future of transport AI – a world where commutes are stress-free, accidents are rare, and our environmental footprint is dramatically minimized. Imagine cities where traffic flows effortlessly, public transport is perfectly synchronized, and personal vehicles are part of a larger, smarter grid. These intelligent ecosystems will learn, adapt, and evolve, continuously improving the quality of urban life and connecting communities like never before.
Shaping Our Collective Journey
As we stand at the cusp of this exciting transformation, it's evident that the evolution of AI-driven transportation is an ongoing journey that requires collective effort. Whether you are a daily commuter experiencing the benefits, an innovator developing the next big breakthrough, or a policymaker crafting the regulatory frameworks, your engagement is crucial. The potential for safer, more efficient, and truly sustainable mobility is immense, but realizing it demands foresight, collaboration, and a willingness to embrace change. Let's actively participate in shaping this hyper-connected future, ensuring it serves humanity's best interests and propels us towards an era of unprecedented mobility and progress. The journey has just begun, and the road ahead is full of possibilities.



Comments (0)
Please login or register to leave a comment.
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!